On 5 April 2022, Microsoft announced the upcoming release of Windows Autopatch. It lets Microsoft take over quality and security patching operations for IT, including Windows operating system feature updates and driver updates. With the planned release in July 2022, Windows Autopatch will be offered as a feature to Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3 license holders.
The offering will work with on-premises, domain-joined devices when using Hybrid Azure AD mode with Microsoft Intune. Windows Autopatch also supports patching operations for Windows 365 for Enterprise users to help support modern work solutions.
NOTE: Windows 365 for Business users aren’t supported.
How does Autopatch work?
Once enabled, Microsoft takes over the patching for your Intune-managed Windows fleet, including automated rollback capabilities in cases where there are problems with updates.
The scope of Windows Autopatch includes selected, but not all, non-Microsoft drivers that would typically get automatically applied. If the driver is optional, it gets published as Manual and does not get automatically supported by Windows Autopatch. IT pros would have to apply those drivers manually, if wanted.
Updates are applied to a small first set of devices, evaluated, and then graduated to increasingly larger sets, with an evaluation period at each progression. This process is dependent on customer testing and verification of all updates during these rollout stages. The outcome is to assure that registered devices are always up to date and disruption to business operations is minimised, which will free an IT department from that ongoing task.
Autopatch deployment model
Windows Autopatch can detect the variations among endpoints in an estate and dynamically create four testing rings. These rings are groups of devices that are representative of all the diversity in an enterprise. The population of these rings is automated – the rings keep their representative samples as devices are added and removed. IT administrators can move specific devices from one ring to another as required or desired.
The diagram illustrates the expected deployment rings model showing the percentage of users in four groups getting software updates.
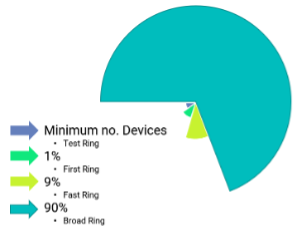
Updates are installed in the ‘test’ ring devices first. After a validation period, if things go well with that group, the software update gets released more broadly to other and larger test groups. This process repeats until a full rollout happens. As more devices receive updates, Autopatch monitors device performance and compares performance to pre-update metrics as well as metrics from the earlier ring, where applicable.
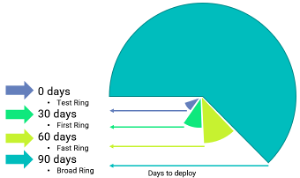
As illustrated below, feature updates that may involve changes to user interfaces or user experience are rolled out more slowly. Each ring is afforded 30 days so users have an opportunity to use the software and report any issues that can’t be detected automatically.
3 key Autopatch capabilities
Windows Autopatch includes a Halt feature that can be started by either Microsoft or the IT Administrators when there are patch problems. A Rollback feature is available for software update failures and can be automatically triggered. Through the Selectivity feature, IT Administrators can allow selected updates to go through and hold back others.
Reporting
Autopatch reporting and messaging capabilities are designed to allow visibility into update status and device health, and offer insights into your estate.
The Autopatch message centre has information about schedules, update status, and details from the Autopatch team. The reporting offers data on update compliance along with device and application performance.
Requirements and prerequisites
Before you get started, it’s good to ensure your current installation is eligible and ready for Autopatch. Here are the requirements and prerequisites you need.
Intune only:
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- Microsoft Intune
- Windows 10/11 supported versions
Co-management:
- Hybrid Azure AD-Joined or Azure AD-joined only
- Microsoft Intune
- Configuration Manager, version 2010 or later
- Switch workloads for device configuration, Windows Update and Microsoft 365 Apps from Configuration Manager to Intune (min Pilot Intune)
- Co-management workloads
How Zetta can help with planning your Autopatch
Zetta has Microsoft Gold Competencies for Cloud Platform, Windows and Devices, and Enterprise Mobility Management. Our team has experience and proven success designing, architecting, implementing, and managing Microsoft Endpoint Management Solutions. We have successfully aided Perth customers with their endpoint management solutions which makes us perfectly poised to help with Autopatch projects.
If you’d like to discuss Windows Autopatch, or explore what it might look like for your organisation, please reach out to the team at Zetta.




